Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-15 Origin: Site











Do you struggle with pressure fluctuations or uneven heating in your hydronic system? Expansion tanks and manifolds are key to controlling pressure and distributing fluid efficiently.
This guide will explain how these components work, their installation, and maintenance. You'll learn how they improve system performance and longevity.
Easywell offers reliable products for expansion tanks securely. Learn more about our products for better system performance.
An expansion tank is a pressure vessel installed in hydronic systems to absorb the increased volume of water when it expands due to heating. As water heats up, it expands, and without an expansion tank, this expansion could cause pressure buildup, leading to leaks or even system failure. Expansion tanks prevent these problems by giving the fluid a place to expand safely.
The expansion tank works by accommodating the increase in water volume when the system heats up. The tank typically contains a diaphragm or bladder that separates the water from a gas (usually air or nitrogen). As water heats and expands, it pushes against the diaphragm, compressing the gas. When the water cools and contracts, the gas pressure pushes the water back into the system, maintaining balanced pressure and preventing damage.
In any closed-loop system, pressure fluctuations can result in significant damage to pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment. Without an expansion tank, these fluctuations could cause pipes to burst, seals to fail, or systems to become less efficient. By absorbing these fluctuations, expansion tanks ensure the system operates safely, reduce the risk of leaks, and extend the lifespan of critical components.
When selecting an expansion tank, several factors must be considered:
● System Volume: The total amount of water in the system, including the pipes, radiators, and boilers, helps determine the required size of the expansion tank.
● Pressure Rating: The expansion tank must be able to withstand the operating pressure of the hydronic system.
● Fluid Type: The type of fluid used (water, glycol, etc.) and its expansion properties must be factored in to select an appropriate tank size.
● Tank Type: Choose between a diaphragm or bladder tank based on the system's needs.
The expansion tank should be sized to accommodate the maximum possible expansion of the fluid in the system. It is typically recommended to size the tank so that it is 25% full when the system is filled with cold fluid. This ensures that there is enough space for fluid expansion during heating.
Installation of the expansion tank should be done near the boiler or heat source, ideally at the highest point in the system. This helps air to be removed efficiently and ensures that the tank operates optimally. The tank should also be easily accessible for regular maintenance.
To ensure the expansion tank is securely positioned, consider using durable expansion tank brackets designed for the environment of your hydronic system. Brackets such as bowed expansion tank mounts are perfect for wet or humid environments, offering corrosion resistance. For residential or standard heating systems, round expansion tank brackets provide a sturdy, adjustable mounting solution that ensures long-term reliability.
Tip: When installing the expansion tank, avoid placing it near heat sources that could cause excessive heating, leading to diaphragm failure.
System Volume (Gallons) | Recommended Expansion Tank Size (Gallons) |
10-20 | 2 |
21-50 | 3 |
51-100 | 5 |
101-200 | 8 |
201-300 | 10 |
301+ | 15+ |
Note: This table is based on general guidelines for system volume and tank sizing. Exact values may vary depending on fluid type and system specifications.

Regular inspections are crucial to ensuring the expansion tank continues to function efficiently. Technicians should check for any leaks, corrosion, or wear on the diaphragm. The pre-charged air pressure should also be checked regularly, as it can decrease over time.
When mounting expansion tanks in environments prone to corrosion, bowed expansion tank brackets offer an extra layer of protection, preventing moisture ingress and ensuring the tank remains stable.
Common issues with expansion tanks include air pressure loss and diaphragm rupture. If the system's pressure gauge fluctuates rapidly, or if water leaks from the tank, these could be signs that the expansion tank needs maintenance or replacement.
A hydronic manifold is a central distribution unit that divides the flow of water from the boiler or heat source into multiple smaller circuits, or "zones." This allows for precise control over the temperature of different areas in the system, such as various rooms or floors in a building. The manifold collects return water from each zone and sends it back to the boiler to be reheated, completing the loop. By balancing the flow in each zone, the manifold helps maintain consistent temperatures throughout the system, improving comfort and energy efficiency.
● Basic Manifolds: These simple units consist of connections that allow multiple loops to be attached. They are generally controlled by external valves and pumps, offering a straightforward solution for smaller or less complex systems. Basic manifolds are typically easier to install and more affordable but may require manual adjustment for optimal performance.
● Smart Manifolds: These advanced units feature built-in flow meters, balancing valves, and actuators that allow for automatic control and adjustment of water flow in each zone. They provide better precision, allowing for more accurate temperature control across multiple zones. Smart manifolds are particularly beneficial in larger or more sophisticated systems where automation and energy efficiency are important.
Manifolds come in various materials, each offering distinct advantages depending on the system’s needs:
● Brass: Known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, brass manifolds are ideal for standard residential or commercial systems that require reliable performance over time. They also provide good resistance to high temperatures and pressure.
● Stainless Steel: Stainless steel manifolds offer superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for systems with high water quality or harsh conditions, such as industrial applications or areas with aggressive water treatment chemicals. Stainless steel is also more robust and can withstand higher pressures and temperatures.
● Plastic: Often used in systems with PEX tubing, plastic manifolds are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion. They are easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for residential heating systems. However, they may not be as durable as brass or stainless steel in harsh environments.
Each type of manifold material offers different strengths, so selecting the right one depends on the specific requirements of your system.
Material | Advantages | Ideal For |
Brass | Durable, corrosion-resistant, high pressure resistance | Standard systems, long-lasting applications |
Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, sleek design | High water quality, harsh environments |
Plastic (PEX) | Lightweight, cost-effective, easy installation | Residential systems, cost-effective solutions |
When selecting the right manifold for your hydronic system, several factors come into play. The size of your system, the number of zones you wish to control, and the type of fluid being used (water, glycol, etc.) are key considerations. For larger systems with multiple zones, it's crucial to choose a manifold that can handle the flow requirements of each zone. If energy efficiency is a primary concern, opt for smart manifolds that allow for better control over each zone, offering automated adjustments based on demand. Additionally, consider the material of the manifold. Materials like brass, stainless steel, and plastic each have unique advantages, with stainless steel offering superior corrosion resistance for systems with high water quality, and plastic being a cost-effective solution for residential setups.
Proper installation and setup of hydronic manifolds are critical for ensuring system efficiency. The manifold should be positioned near the heat source to minimize pressure losses. All connections between the manifold and piping must be secure to avoid leaks. Ensuring that all valves are properly adjusted and balanced is essential so that each zone receives the right amount of heat. A balanced manifold ensures uniform temperature distribution across the system, preventing hot or cold spots. Additionally, installing air purging valves is highly recommended. These valves allow for the efficient removal of trapped air, which can reduce the overall efficiency of the system and lead to improper heating. Proper installation and regular maintenance of the manifold system can significantly enhance the lifespan and performance of your hydronic system.
.
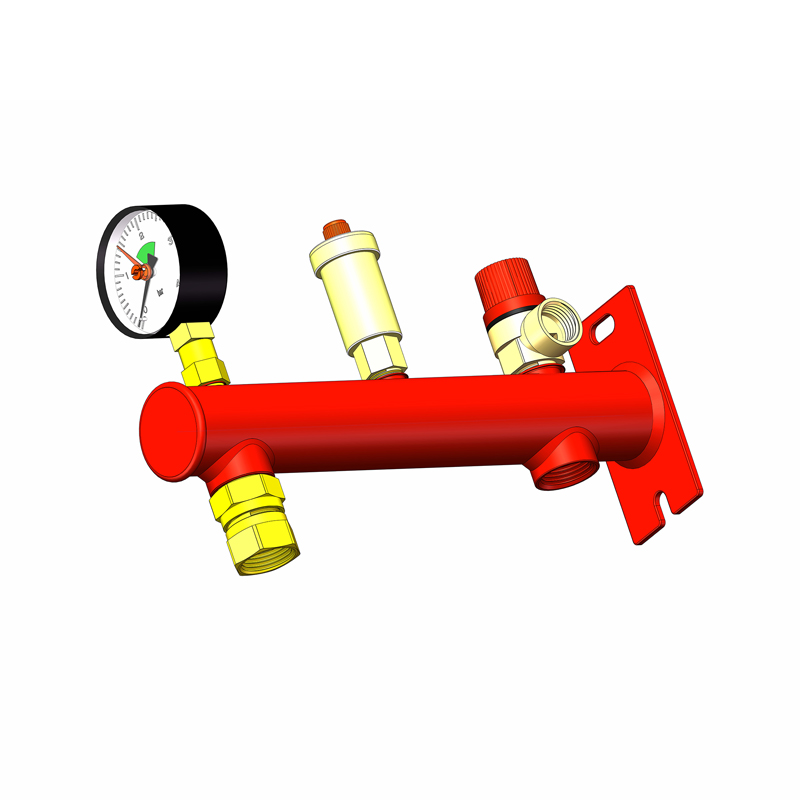
To keep the manifold operating efficiently, it's essential to perform regular checks. Look for any blockages in the pipes, air in the lines, or stuck valves. These issues can hinder the system’s performance, causing uneven heating and poor flow. Additionally, periodically clean the system to prevent debris buildup, which can reduce efficiency or cause blockages. A well-maintained manifold ensures optimal fluid distribution and maintains consistent heating or cooling across all zones.
Common manifold issues include uneven heating, air in the system, and stuck valves, which can lead to imbalanced water flow. If you're experiencing these problems, start by inspecting the valves to ensure they are functioning correctly. Balancing the system is key to ensuring that each zone gets the appropriate amount of heat. For air-related problems, purging the air from the lines is essential. Regular maintenance and quick troubleshooting can help prevent more serious issues and maintain system performance.
Expansion tanks play a critical role in maintaining steady pressure within hydronic systems. By absorbing fluctuations in pressure caused by the thermal expansion of water, they prevent excessive stress on the system's components. This helps the system run more smoothly and efficiently, reducing the load on pumps and other key components. As a result, the overall energy consumption is lower, leading to significant cost savings over time. Additionally, properly installed expansion tanks can extend the lifespan of equipment, further reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Hydronic manifolds, particularly advanced smart manifolds, contribute significantly to energy efficiency by optimizing water flow across different zones. These manifolds ensure that each zone receives only the necessary amount of water, preventing overuse or waste of energy. By maintaining a consistent and balanced temperature throughout the system, smart manifolds help reduce energy consumption and improve comfort. This efficient management of heat distribution not only leads to lower energy bills but also minimizes the wear and tear on the system, resulting in cost savings and improved performance.
Expansion tanks and manifolds are essential for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of hydronic systems. Proper installation and maintenance of these components can extend the system’s lifespan, reduce energy costs, and improve comfort. In environments prone to corrosion, Easywell's expansion tank brackets provide added protection, keeping tanks secure and free from corrosion. For residential or modular systems, Easywell's adjustable and square brackets offer reliable, space-saving solutions. Regular maintenance of these components helps prevent costly repairs, making the right choice a long-term investment.
A: Expansion tanks absorb pressure caused by the thermal expansion of water in hydronic systems. They help maintain steady system pressure, preventing damage to pipes and valves.
A: Hydronic manifolds distribute water evenly across multiple zones, ensuring balanced flow and consistent temperature. This helps optimize system efficiency and energy use.
A: Choosing the right size expansion tank ensures optimal pressure regulation and prevents damage. An undersized tank can lead to pressure fluctuations, while an oversized one can waste space and energy.
A: Regularly inspect and clean expansion tanks and manifolds. Check pressure settings, ensure no leaks, and keep valves free from blockages to ensure efficient operation and prevent costly repairs.